Header Menu
Can this smoothie naturally relieve joint pain?
Tuesday, March 26, 2019 by Amy Goodrich
http://www.naturalnewsrecipes.com/2019-03-26-this-smoothie-naturally-relieve-joint-pain.html
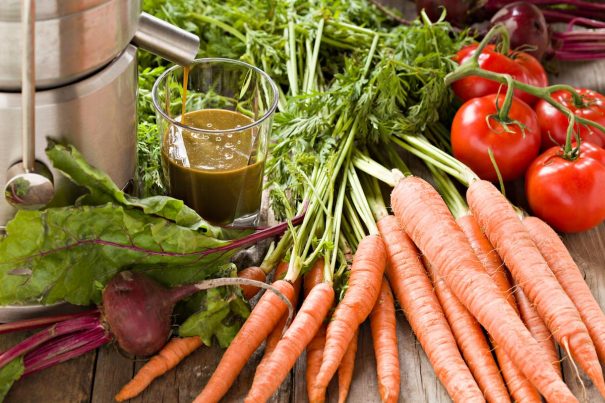

While joint pain and arthritis are more common among the elderly, both young and old can suffer from this condition, and debilitating pain can severely affect the quality of life. Therefore, many people resort to over-the-counter drugs or prescription medication. These drugs can temporarily bring relief to pain sufferers. But in the long run, they can lead to dependency and drug addiction.
For this reason, many doctors and wellness experts now encourage people to use natural healing superfoods to rid the body of chronic inflammation and pain.
Whether it’s a stiff hip joint, a sore elbow or gout in a big toe, millions of people each year find themselves suffering from joint pain. Instead of putting all your hopes on damaging drugs, natural health experts recommend drinking the pain-relieving smoothie below for optimal joint functioning and pain reduction.
Pain-relieving smoothie recipe
This antioxidant-rich smoothie is chock full of natural ingredients that help reduce inflammation, joint pain and other arthritic symptoms.
Ingredients
- ¼ organic lemon, no need to peel
- ½ piece fresh turmeric root, peeled
- ½ piece fresh ginger root, peeled
- 1 red apple, cored
- 3 to 4 carrot pieces
- A pinch of fresh ground black pepper
- Filtered water
Note that turmeric’s active compound, curcumin, isn’t easily absorbed by the body. Fortunately, there is a simple kitchen spice that you can use to boost turmeric’s bioavailability. Adding a pinch of black pepper to this smoothie can increase the absorption of turmeric’s active compound by up to 2,000 percent.
Directions
- Cut all the ingredients into small pieces and add them to a blender or slow juicer.
- Add filtered water and blend until desired consistency.
- Drink this smoothie, or juice, first thing in the morning for optimal joint health.
Here’s how each ingredient improves the smoothie’s effectiveness
Turmeric — Curcumin, turmeric’s active compound, is well known for its ability to fight chronic inflammation and pain caused by arthritis. One study, published in the journal Clinical Interventions in Aging, found curcumin extract to be as effective as ibuprofen in treating chronic pain. Furthermore, turmeric users experienced fewer side effects. Another study, published in the journal Phytotherapy Research, found turmeric to be safe and efficient in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Additionally, Healthy Builderz reported that turmeric can successfully be used as a natural remedy to alleviate symptoms linked to chronic medical conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and multiple sclerosis.
Ginger — Another incredible root known to reduce joint pain and inflammation in people diagnosed with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, ginger’s active compounds suppress inflammation-causing molecules by switching off certain inflammatory genes. Just like turmeric, ginger has been shown to be as effective as ibuprofen without adding any side effects.
Apples — Apples are an excellent source of quercetin, an anti-inflammatory antioxidant. In addition to reducing inflammation and fighting chronic pain, quercetin may also prevent heart disease, lower cholesterol levels and improve circulation.
Carrots — Rich in beta-carotene, beta-cryptoxanthin and other powerful antioxidants, carrots can fight inflammation better than ibuprofen, aspirin and Celebrex.
Lemon — While the whole lemon is beneficial to overall health, its skin houses the most active compounds to relax blood vessels, reduce inflammation and alleviate nerve pain. Be sure to use organic lemons to avoid pesticides and other nasty chemicals entering your body.
If you or one of your loved ones suffers from chronic pain, don’t hesitate to try this delicious homemade smoothie. The combination of ingredients provides a natural, healing solution for joint pain. It is also vitally important to support your joints and overall health with proper nutrition and avoid inflammation-causing foods high in processed sugars, grains and fats.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: anti-inflammatory, antioxidants, arthritis, chronic pain, food cures, food is medicine, Fresh, functional food, goodfood, goodhealth, goodmedicine, inflammation, joint pain, organics, pain relief, smoothie, superfoods